論文がアクセプトされました(山崎先生)
Effect of Mixed Valence States of Platinum Ion Dopants on the Photocatalytic
Activity of Titanium Dioxide under Visible Light Irradiation
N. Nishiyama, S. Yamazaki
ACS Omega, 2017, 2, 9033-9039.
DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01393
Abstract: Titanium dioxide doped with the Pt ion (Pt–TiO2) was synthesized by a
sol–gel method using only water as the solvent and conducting dialysis.
The photocatalytic activity for the degradation of 4-chlorophenol (4-CP)
on Pt–TiO2 was not affected by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller specific surface
area under visible light (VL) irradiation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
(XPS) and X-ray absorption near-edge structure measurements revealed that
only the Pt(IV) ion existed in the TiO2 bulk and both Pt(II) and Pt(IV)
were present near the Pt–TiO2 surface. Pt(IV) is most likely substituted
in the Ti(IV) site of the TiO2 lattice because of their similar ionic sizes.
Quantitative analysis of Pt(II) was performed in the XPS measurements,
indicating that the amount of Pt(II) on the surface increased with an increase
in the doping amount from 0.2 to 1.0 atom %. We synthesized 0.5 atom %
Pt–TiO2 with various Pt(II)/Pt(IV) ratios by changing the Ti(OC3H7)4 concentration
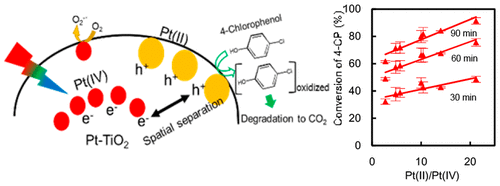
used in the sol–gel synthesis. The 4-CP conversion on Pt–TiO2 increased
linearly with an increase in the Pt(II)/Pt(IV) ratios. A similar relationship
was obtained with Pt–TiO2, which was prepared by a conventional sol–gel
method in ethanol–water mixed solvent. Therefore, the Pt(II)/Pt(IV) ratio
is a key factor affecting the photocatalytic activity of Pt–TiO2 under
VL irradiation. Our results indicate that controlling the mixed valence
states of the doped metal ions is a new strategy to developing highly active
metal-ion-doped TiO2 under VL irradiation.