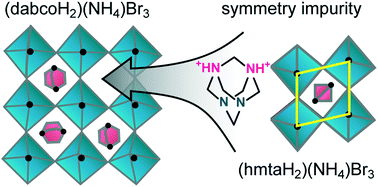
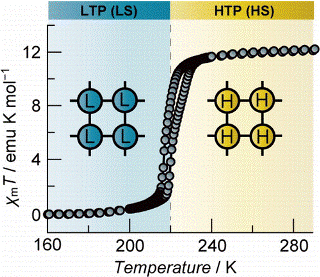
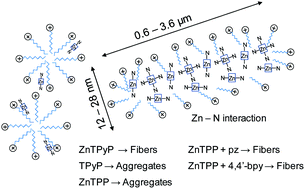
Ni- and Cu-co-Intercalated Layered Manganese Oxide for Highly Efficient
Electro-Oxidation of Ammonia Selective to Nitrogen
K. Nagita, Y. Yuhara, K. Fujii, Y. Katayama, M. Nakayama
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 28098-28107.
DOI : 10.1021/acsami.1c04422
Abstract: We fabricated a thin film of layered MnO2 whose interlayer space was occupied
by hydrated Ni2+ and Cu2+ ions. The process consisted of electrodeposition
of layered MnO2 intercalated with tetrabutylammonium cations (TBA+) by
anodic oxidation of aqueous Mn2+ ions in the presence of TBA+, followed
by ion exchange of the initially incorporated bulkier TBA+ with the denser
transition metals in solution. The resulting layered MnO2 co-intercalated
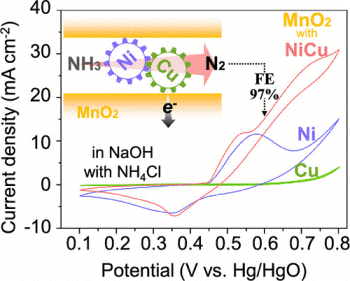
with Ni2+ and Cu2+ ions (NiCu/MnO2) catalyzed the ammonia oxidation reaction
(AOR) in an alkaline electrolyte with a much lower overpotential than its
Ni2+- and Cu2+-intercalated single-cation counterparts. Surprisingly, the
NiCu/MnO2 electrode achieved a faradic efficiency as high as nearly 100%
(97.4%) for nitrogen evolution at a constant potential of +0.6 V vs Hg/HgO.
This can be ascribed to the occurrence of the AOR in the potential region
where water is stable and dimerization of the partially dehydrogenated
ammonia species is preferred, thereby forming an N–N bond, rather than
to be further oxidized into NOx species.