論文がアクセプトされました(本多先生)
Amorphous Carbon Having Higher Catalytic Activity toward Oxygen Reduction
Reaction: Quinone and Carboxy Groups Introduced onto its Surface
K. Honda, Y.Waki, A.Matsumoto, B. Kondo, Y. Shimai
Diam. Relat. Mater., 2020, 107, 107900.
DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2020.107900
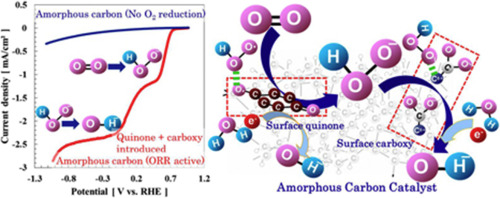
Abstruct: Amorphous carbon (a-C) based catalysts having higher activity and stability
for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) were achieved by introducing quinone
and carboxy groups onto a-C surfaces. The surface-bonded quinone groups
increased the rate of ORR to hydrogen peroxide. The surface carboxy groups
promoted the activity toward electrochemical peroxide reduction. However,
few studies have reported on their contribution. ORR activity was controlled
by varying density of quinone and carboxy groups on the a-C surfaces. The
ORR activity was proceeded by 2 + 2 electron mechanism through H2O2 that
acted as an intermediate. The number of electrons transferred per O2 molecule
reached 4.08 at a maximum. The catalytic activity of the catalyst was stable
in long term measurements (150 times in 20 h) because a-C inherently has
high corrosion resistance and oxygen-contained surface functionalities
are stable in aqueous solution. Consequently, the a-C catalysts possessed
high ORR reproducibility.