論文がアクセプトされました(山崎先生)
Photocatalytic Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol on Titanium Dioxide Modified
with Cu(II) or Cr(III) Ion under Visible Light Irradiation
N. Nishiyama, K. Kozasa, S. Yamazaki
Appl. Catal. A: General, 2016, 527, 109-115.
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2016.09.001
Abstract: TiO2 modified with Cu2+ or Cr3+ ion (M-TiO2, M-grafted TiO2) was synthesized
by a sol-gel method using Ti(OC3H7)4 as a starting material or a graft
method by impregnation of rutile TiO2. In the sol-gel method, the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller
(BET) surface area of M-TiO2 was varied by preparing with or without dialysis
of TiO2 sol (M-TiO2(D) or M-TiO2(ND), respectively). Even by using the
sol-gel method, Cu2+ whose ionic size is larger than Ti4+ cannot be doped
but is incorporated in TiO2 due to relatively weak interaction. Dissolution
of Cu2+ ion was observed when Cu-TiO2(D), Cu-TiO2(ND) or Cu-grafted TiO2
was immersed into the acidic solution of 0.1 mol dm−3 HCl. The photocatalytic
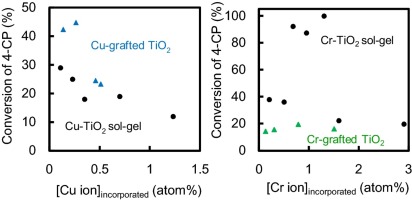
activity for the degradation of 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) under visible light
irradiation was the following order: Cu-grafted TiO2 > Cu-TiO2(ND) >
Cu-TiO2(D). We have revealed that the photocatalytic activity of Cu-grafted
TiO2 decreases linearly with an increase in the number-density of Cu2+
ion on the TiO2 surface. On the other hand, in the case of Cr3+ ion which
has a similar size as Ti4+, the photocatalytic activity increased remarkably
by doping Cr3+ in TiO2 by the sol-gel method. An increase in the BET surface
area by conducting dialysis enhanced the photocatalytic activity. This
paper demonstrates from the viewpoint of the higher photocatalytic activity
as well as the chemical stability in acidic conditions that Cr-doped TiO2
prepared by the sol-gel method gives an advantage over Cu-grafted TiO2
for the degradation of 4-CP which is one of the non-degradable organic
contaminants in water.