論文がアクセプトされました(石井先生)
Compartmentalization of Gold Nanoparticle Clusters in Hollow Silica Spheres
and Their Assembly Induced by An External Electric Field
K. Watanabe, T.A.J. Welling, S. Sadighikia, H. Ishii, A. Imhof, M.A.van Huis, A. Blaaderen, D. Nagao
J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2020, 566, 202-210.
DOI : 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.01.094
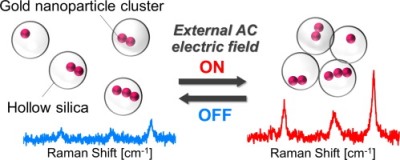
Abstract: Assembly of plasmonic nanoparticle clusters having hotspots in a specific
space is an effective way to efficiently utilize their plasmonic properties.
In the assembly, however, bulk-like aggregates of the nanoparticles are
readily formed by strong van der Waals forces, inducing a decrease of the
properties. The present work proposes an advanced method to avoid aggregation
of the clusters by encapsulating into a confined space of hollow silica
interior. Hollow spheres incorporating gold nanoparticle clusters were
synthesized by a surface-protected etching process. The observation of
inner nanoparticles with liquid cell transmission electron microscopy experimentally
proved that the nanoparticles moved as a cluster instead of as dispersed
nanoparticles within the water-filled hollow compartment. The hollow spheres
incorporating the nanoparticle clusters were assembled in the vicinity
of electrodes by application of an external AC electric field, resulting
in the enhancement of Raman intensities of probe molecules. The nanoparticle-cluster-containing
hollow spheres were redispersed when the electric field was turned off,
showing that the hollow silica spheres can act as a physical barrier to
avoid the cluster aggregation. The Raman intensities were reversibly changed
by switching the electric field on and off to control the assembled or
dispersed states of the hollow spheres.