論文がアクセプトされました(K_藤井先生)
Fluorinated Alkyl-Phosphate-Based Electrolytes with Controlled Lithium-Ion
Coordination Structure
S. Sawayama, Y.M. Todorov, H. Mimura, M. Morita, K. Fujii
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21, 11435-11443.
DOI : 10.1039/C9CP01974J
Abstract: Herein, we propose Li-ion solvation-controlled electrolytes based on non-flammable
organic solvent TFEP and an LiFSA salt [TFEP: tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)phosphate,
LiFSA: lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)amide] to allow Li-ion insertion into
a graphite electrode for Li-ion batteries. Comprehensive structural study
based on (1) infrared (IR)/Raman spectroscopy, (2) high-energy X-ray total
scattering (HEXTS), and (3) molecular dynamics (MD) simulation revealed
the solvation (or coordination) structures of Li ions in TFEP-based electrolytes
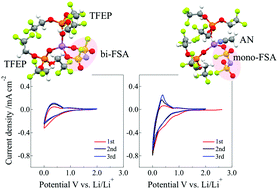
at the molecular level. In binary LiFSA/TFEP with a Li salt concentration
(cLi) < 1.0 mol dm−3, Li ions are coordinated with both TFEP and FSA
components; in detail, two TFEP molecules coordinate in an O-donating monodentate
manner and one FSA in an O-donating bidentate manner to form [Li(TFEP)2(bi-FSA)]
as the major species. We demonstrated that adding acetonitrile (AN) to
the LiFSA/TFEP electrolytes caused structural changes in the Li-ion complexes.
The bi-FSA bound to the Li ion changed its coordination mode to mono-FSA,
which was induced by solvating AN molecules to Li ions. The redox reaction
corresponding to insertion/deinsertion of Li ions into/from the graphite
electrode successfully occurred in 1.0 mol dm−3 LiFSA/TFEP with an AN electrolyte
system, while there was no or reduced Li-ion insertion in the electrolyte
without AN. We discussed the relationship between the structure and electrode
reaction of the Li-ion complexes based on the FSA-coordination characteristics;
i.e., in LiFSA/TFEP with the AN system, the mono-FSA bound to the Li ion
is easier to decoordinate due to weaker Li+⋯mono-FSA− interactions rather
than the Li+⋯bi-FSA− interactions, which mainly contribute to charge-transfer
at the electrode/electrolyte interface to allow Li-ion insertion/deinsertion
in the graphite anode.